
SPF DKIM Records: Your Complete Guide to Email Authentication That Actually Works
- Sophie Ricci
- Views : 28,543
Table of Contents
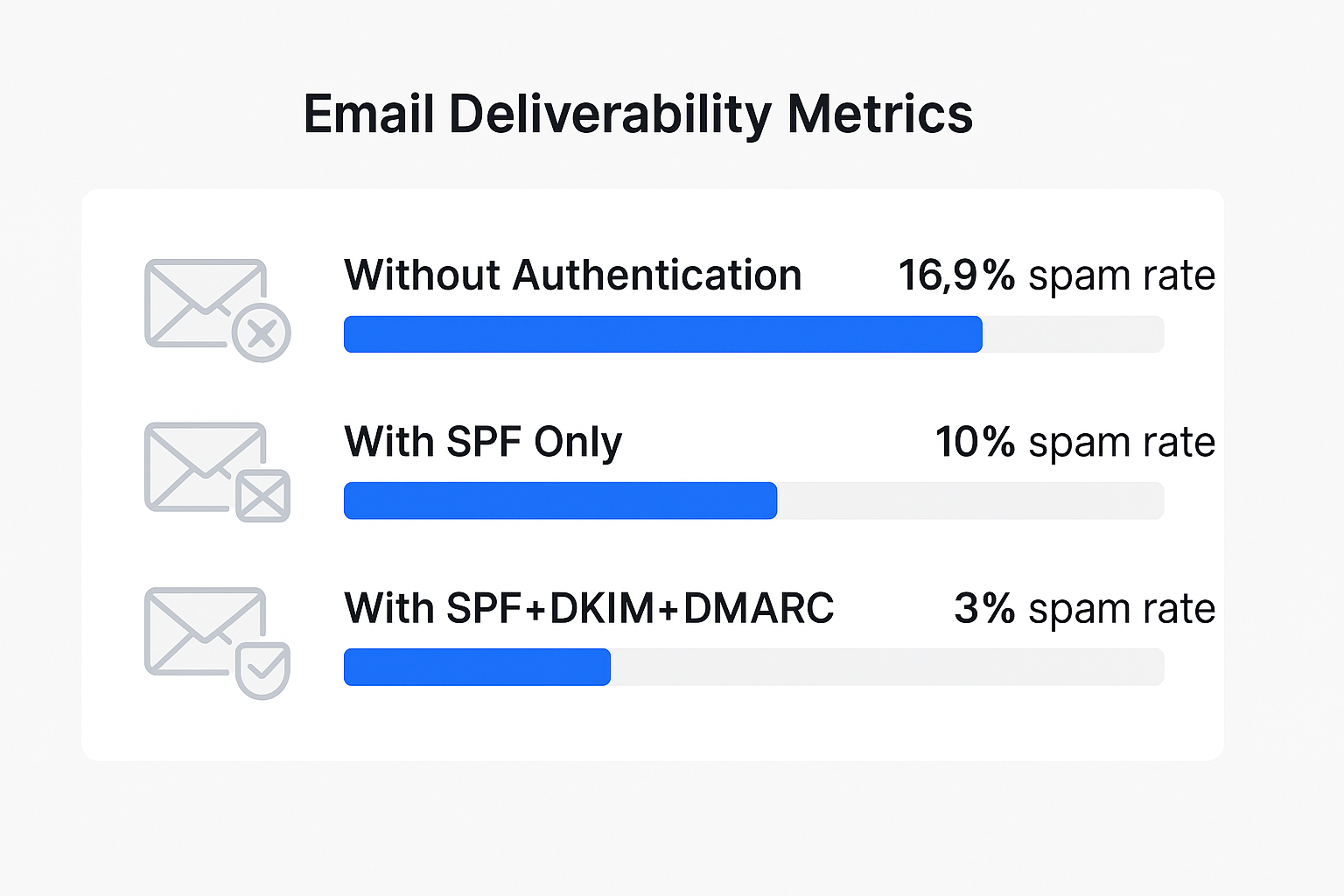
Ever sent a perfectly crafted email only to have it vanish into the spam folder? You’re not alone. 16.9% of all emails never reach the primary inbox, and the culprit isn’t your subject line—it’s missing email authentication.
📧 Tired of Email Deliverability Issues?
LinkedIn outbound bypasses spam filters entirely—reach decision-makers with 89% open rates guaranteed
Without proper spf dkim records, your emails are essentially strangers knocking on your prospects’ doors with no ID. Email providers like Google and Microsoft won’t take chances—they’ll send you straight to spam or block you entirely.
This guide breaks down everything you need to know about spf dkim dmarc authentication in simple terms. By the end, you’ll have your domain properly secured and your emails landing where they belong: the inbox.
What do DKIM, SPF, and DMARC stand for in email security?
Think of email authentication like airport security—multiple checkpoints ensure only legitimate passengers (emails) reach their destination.
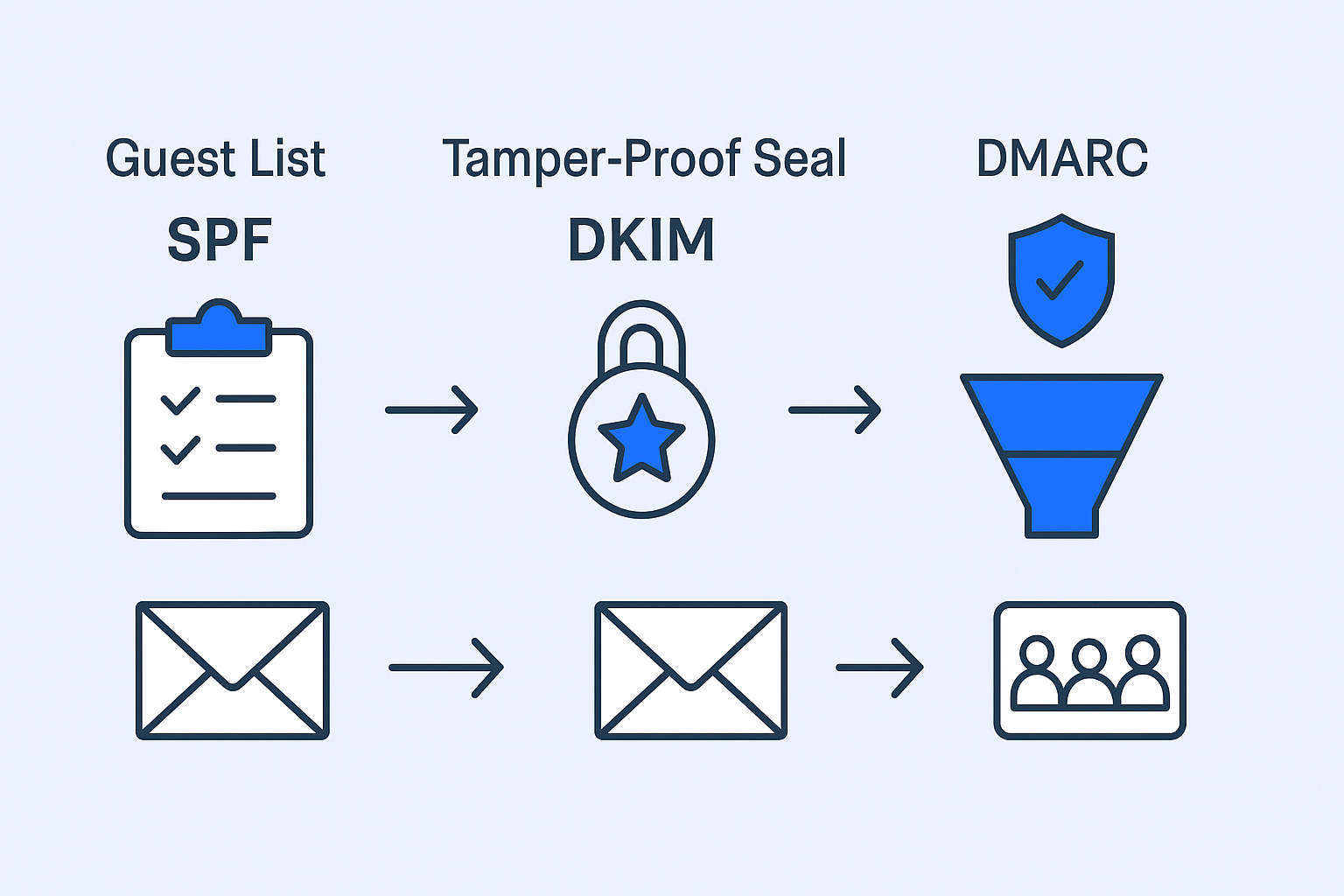
🛡️ SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
SPF record acts like an official guest list at a high-security event. When your email arrives at Gmail or Outlook, they check: “Is this sender on the approved list?”
SPF is a simple text file published in your domain’s DNS settings that lists all IP addresses and services authorized to send emails on your behalf. According to recent studies, 85% of domains have some form of SPF record, but many are misconfigured.
🔒 DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail)
DKIM functions as a tamper-proof seal on your email package. Domainkeys identified mail adds a unique digital signature to every email you send, created with a private key only your server knows.
The receiving server uses your public key (published in DNS) to verify the seal hasn’t been broken. If the signature matches, your email is trusted as authentic and unaltered during transit.
🚀 DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance)
DMARC is the security chief who makes the final call. It looks at both SPF and DKIM results and enforces your predetermined policy. But here’s the crucial part—it also sends you detailed reports showing who’s sending emails from your domain.
DMARC adoption has increased by 200% over the past two years, yet 70% of businesses still don’t have it properly configured.
🎯 Avoid Technical Authentication Complexity
Our LinkedIn outbound engine targets, engages, and converts prospects without DNS configuration nightmares
Why are DKIM, SPF, and DMARC necessary? Let’s explore!
The Trust Factor That Controls Your Inbox Placement
Email providers process over 333 billion emails daily. Their algorithms rely heavily on sender reputation to decide inbox placement. Properly configured spf dkim authentication is the foundation of that reputation.
Industry data shows that domains with complete authentication see 10% higher deliverability rates with major providers. That’s thousands more emails reaching prospects each month.
Protection Against Domain Spoofing
Without authentication, anyone can send emails pretending to be your company. 3.4 billion phishing emails are sent daily, and if scammers use your domain, it destroys your sender reputation instantly.
The average cost of a data breach from email-based attacks has reached $4.88 million. Setting up dkim dmarc protection isn’t just about deliverability—it’s about protecting your business.
It’s Now Mandatory, Not Optional
As of 2024, Google and Yahoo require email authentication for anyone sending bulk emails (more than 5,000 messages per day). Even smaller senders are strongly encouraged to implement these protocols to avoid deliverability issues.
How to Set up DKIM, SPF, and DMARC: A Guide
DKIM, How to set it up?
📺 Video Guide: Most email providers offer visual setup guides in their admin panels.
🪜 Steps to Follow:
- Access your email provider’s admin console
- Google Workspace: Admin Console > Apps > Gmail > Authenticate email
- Microsoft 365: Admin Center > Exchange > Mail flow > Domains
- Generate your DKIM keys
- Choose 2048-bit key length for maximum security
- Your provider will generate a “selector” (like google._domainkey) and a long public key string
- Add the TXT record to your DNS
- Host/Name: [selector]._domainkey.yourdomain.com
- Value: The long DKIM public key provided
- TTL: 3600 seconds (default)
- Enable DKIM in your email provider
- Return to your admin console and activate DKIM signing
- Changes may take up to 48 hours to propagate globally
Troubleshooting DKIM Setup Issues:
- Key too long: Some DNS providers have character limits. Break long keys into multiple quoted strings.
- Authentication still failing: Use an spf dkim record check tool like MXToolbox to verify your setup.
- Propagation delays: DNS changes can take 24-48 hours. Be patient before testing.
SPF, How to set it up?
📺 Video Guide: Check your domain registrar’s help documentation for DNS management tutorials.
🪜 Steps to Follow:
- Identify all email sending sources
- Your primary email provider (Google, Microsoft, etc.)
- Marketing tools (Mailchimp, Klaviyo, etc.)
- Sales tools and CRM systems
- Any third-party services that send on your behalf
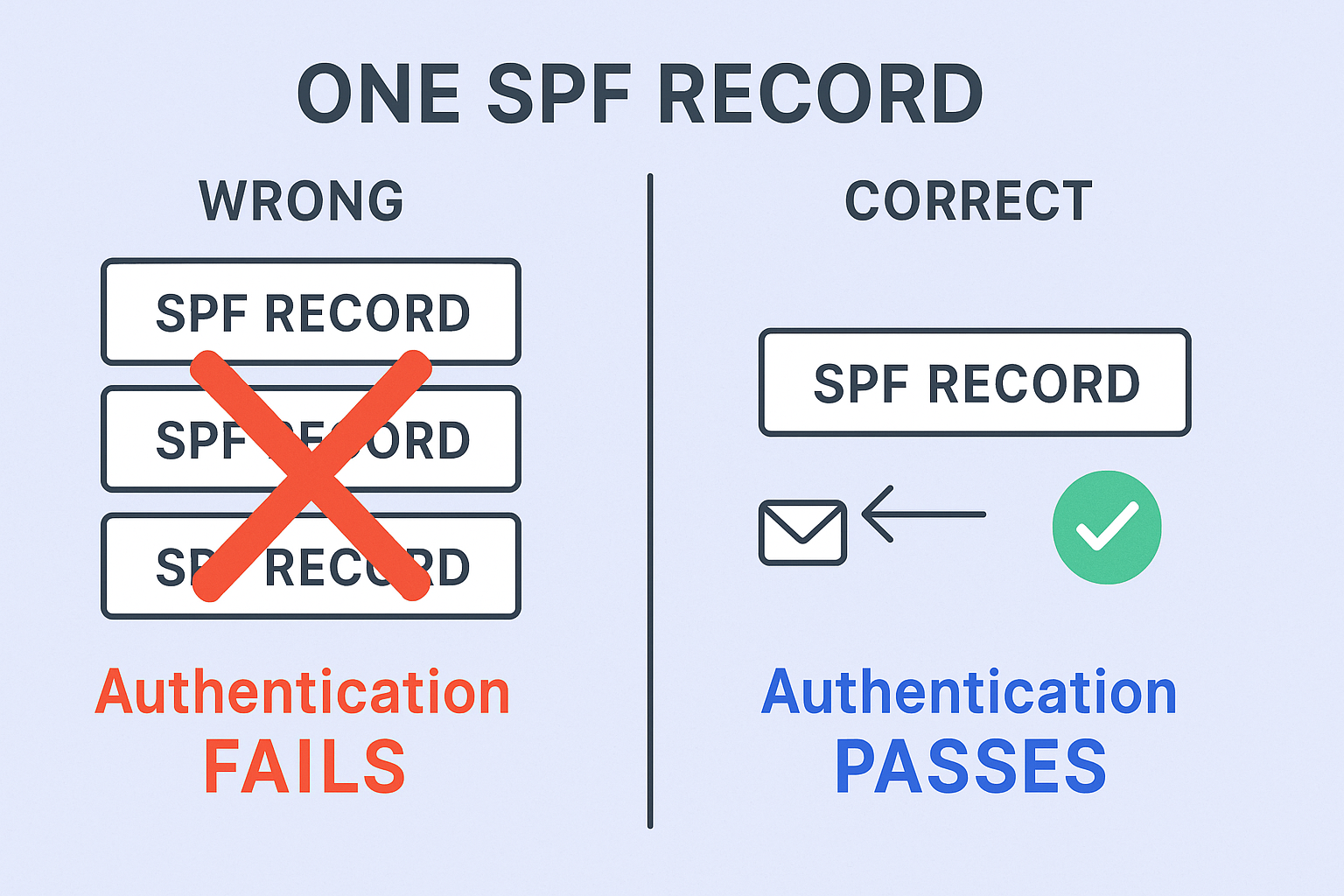
- Create your SPF record ⚠️ Critical Rule: Only ONE SPF record per domain
Basic format: v=spf1 include:_spf.google.com ~all
Common includes to add:- Google Workspace: include:_spf.google.com
- Microsoft 365: include:spf.protection.outlook.com
- Mailchimp: include:servers.mcsv.net
- Add TXT record to DNS
- Host/Name: @ (represents your root domain)
- Value: Your complete spf record
- TTL: 3600 seconds
- Test your SPF record
- Use online SPF validators to check syntax
- Ensure you stay under the 10 DNS lookup limit
- Verify all sending sources are included
DMARC, how to set it up?
📺 Video Guide: DMARC setup requires careful planning—video tutorials help visualize the phased approach.
🚀 Skip the 48-Hour Wait
LinkedIn campaigns launch in 24 hours with our complete targeting, creative, and scaling strategy
🪜 Steps to Follow:
Phase 1: Monitor Mode (Start Here)
- Create initial DMARC policy
- Host/Name: _dmarc
- Value: v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:dmarc-reports@yourdomain.com
- This monitors all activity without blocking emails
- Set up report collection
- Create a dedicated email address for DMARC reports
- Reports arrive daily showing all authentication activity
- Use DMARC analyzer tools to interpret data
Phase 2: Gradual Enforcement (After 2-4 weeks) 3. Analyze report data
- Identify all legitimate sending sources
- Look for authentication failures from your own systems
- Spot potential spoofing attempts
- Upgrade to quarantine policy
- Change to p=quarantine to send failing emails to spam
- Monitor for any legitimate emails being affected
- Final step: Reject policy
- Upgrade to p=reject for maximum protection
- This blocks unauthenticated emails completely
- Only do this when confident all legitimate sources pass
DMARC Policy Progression:
Policy | What It Does | When to Use |
p=none | Monitor only, no enforcement | Starting point (weeks 1-4) |
p=quarantine | Send failures to spam folder | Intermediate step (after analysis) |
p=reject | Block failures completely | Final goal (maximum protection) |
Before You Send Emails
Wait for DNS Propagation
Never send bulk emails immediately after DNS changes. Wait 48 hours for global propagation. Sending too early can damage your sender reputation.
💼 Ready to Scale Faster?
Our LinkedIn outbound system delivers qualified meetings from day one—no warm-up period required
7-day Free Trial |No Credit Card Needed.
Use Email Testing Tools
- Mail-Tester.com: Send a test email and get a deliverability score
- MXToolbox: Verify your spf dkim records are properly configured
- Google Postmaster Tools: Monitor your domain’s reputation with Gmail
Verify Authentication in Email Headers
Check any received email’s headers for:
- spf=pass
- dkim=pass
- dmarc=pass
All three should show “pass” for proper authentication.
Start with Email Warm-up
Even with perfect authentication, new domains need gradual volume increases. Start with 50 emails per day and slowly increase over 2-3 weeks.
Key Takeaways for Email Authentication
Authentication is now mandatory. Major email providers require spf dkim dmarc for bulk senders. Without it, your emails simply won’t be delivered.
One SPF record per domain. This is the most common setup mistake. Multiple SPF records will cause authentication to fail completely.
Start DMARC with p=none. Always begin in monitoring mode to avoid accidentally blocking legitimate emails while you fine-tune your setup.
Test before sending. Use tools like mail-tester.com to verify your configuration before launching campaigns. A perfect 10/10 score should be your goal.
Monitor your reputation. Set up Google Postmaster Tools and monitor your email deliverability statistics regularly to catch issues early.
Be patient with DNS. Changes can take up to 48 hours to propagate worldwide. Rushing the process can harm your sender reputation.
Remember, proper email authentication isn’t just about following technical requirements—it’s about building trust with email providers and ensuring your messages reach the people who need them. With 16.9% of emails never reaching the inbox, can you afford not to have proper authentication?
The setup might seem technical, but the impact on your email success is immediate and measurable. Once configured, you’ll see higher delivery rates, better engagement, and most importantly, your emails will start landing in the primary inbox where they belong.
Whether you’re sending cold email campaigns, nurturing leads, or following up with prospects, proper authentication is your foundation for email success. Don’t let poor deliverability sabotage your outreach efforts—get your spf dkim records configured correctly, and watch your inbox placement rates soar.
Other Useful Resources
With 16.9% of emails never reaching inboxes and 70% of businesses struggling with DMARC configuration, maintaining email deliverability requires constant vigilance. For teams building email prospecting infrastructure, our Email Extractor guide and Mail Tester Alternative review help verify contacts and test authentication before launching campaigns that depend on perfect SPF, DKIM, and DMARC alignment.
As email authentication becomes mandatory and DNS propagation delays impact campaign timelines, many teams are diversifying to LinkedIn where no technical setup is required. Explore industry-specific strategies like LinkedIn Prospecting for Financial Advisors, discover LinkedIn Prospecting AI tools for automated targeting, or partner with a LinkedIn Prospecting Agency for done-for-you campaigns that launch in 24 hours—no 48-hour DNS wait required.
For professionals optimizing their LinkedIn presence, review LinkedIn Premium Job Seeker benefits and explore our LinkedIn Singapore Statistics to understand regional engagement patterns critical for teams running global outreach without email authentication headaches.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if I don't set up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC?
Can I have multiple SPF records for one domain?
How long does it take for DNS changes to take effect?
What's the difference between SPF and DKIM?
Should I start with DMARC policy p=reject immediately?
We deliver 100–400+ qualified appointments in a year through tailored omnichannel strategies
- blog
- Sales Development
- SPF DKIM Records Guide: Setup Email Authentication 2025


